The Database of Interacting Proteins (DIP: http://dip.doe-mbi.ucla.edu) is a database that paperwork experimentally decided protein-protein interactions. It offers the scientific group with an built-in set of instruments for looking and extracting details about protein interplay networks.
As of September 2001, the DIP catalogs roughly 11 000 distinctive interactions amongst 5900 proteins from>>80 organisms; the overwhelming majority from yeast, Helicobacter pylori and human. Tools have been developed that enable customers to research, visualize and combine their very own experimental information with the details about protein-protein interactions obtainable in the DIP database.
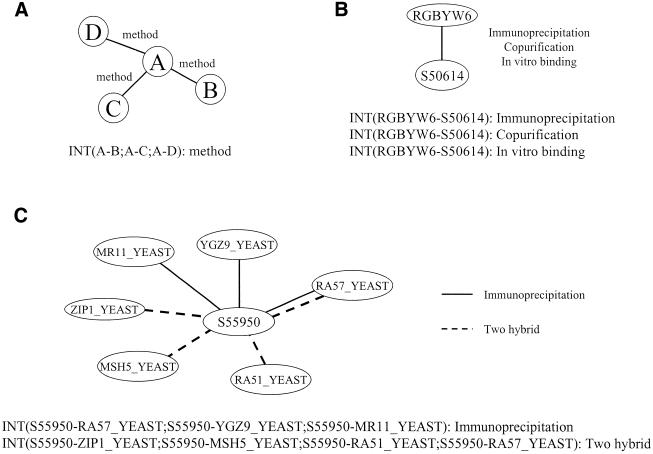
DIP, the Database of Interacting Proteins: a research tool for studying cellular networks of protein interactions.
Validation of the National Health Insurance Research Database with ischemic stroke circumstances in Taiwan.
OBJECTIVEThe National Health Insurance Research Database (NHIRD) is often used for pharmacoepidemiological research in Taiwan. This examine evaluated the validity of the database for sufferers with a principal analysis of ischemic stroke.METHODSThis cross-sectional examine compares data in the NHIRD with these in a single medical middle.
Patients hospitalized for ischemic stroke in 1999 had been recognized from each databases. The discharge notes, laboratory information, and medicine orders throughout admission and the first discharge go to had been reviewed to validate ischemic stroke diagnoses and aspirin prescribing in the NHIRD.
Agreement between the two databases in comorbidities of ischemic stroke analysis was evaluated utilizing ICD-9 codes.RESULTSThree hundred and seventy two circumstances had been recognized from the NHIRD; amongst them, 364 circumstances (97.85%) had been confirmed as ischemic stroke by radiology examination and medical presentation.
Among these confirmed circumstances, 344 (94.51%) had been assigned ‘ischemic stroke’ as the principal analysis in the NHIRD. The total settlement of comorbid diagnoses between the databases was 48.39%. The PPV for chosen situations additionally diversified broadly, from 0.50 for fracture to 1.00 for colon most cancers. The accuracy of recorded aspirin prescriptions was greater in first post-discharge visits (PPV = 0.94) than throughout hospitalization (PPV = 0.88).
CONCLUSIONSThe accuracy of the NHIRD in recording ischemic stroke diagnoses and aspirin prescriptions was excessive, and the NHIRD seems to be a legitimate useful resource for inhabitants research in ischemic stroke.
A overview of makes use of of well being care utilization databases for epidemiologic research on therapeutics.
OBJECTIVELarge well being care utilization databases are incessantly utilized in selection of settings to check the use and outcomes of therapeutics. Their measurement permits the examine of rare occasions, their representativeness of routine medical care makes it potential to check real-world effectiveness and utilization patterns, and their availability at comparatively low value with out lengthy delays makes them accessible to many researchers. However, issues about database research embrace information validity, lack of detailed medical info, and a restricted potential to regulate confounding.
METHODSWe take into account the strengths, limitations, and applicable functions of well being care utilization databases in epidemiology and well being providers research, with specific reference to the examine of medicines.CONCLUSIONSProgress has been made on many methodologic points associated to the use of well being care utilization databases lately, however necessary areas persist and benefit scrutiny.
